Capybara
Capybara are very big rodents,rodents, in fact, the biggestbiggest rodents in the world, as big as large dogs. An adult can be over 60 centimetrescentimetres in height, 130 centimetres in length, and can weigh as much as 66 kilograms.Where Capybara Live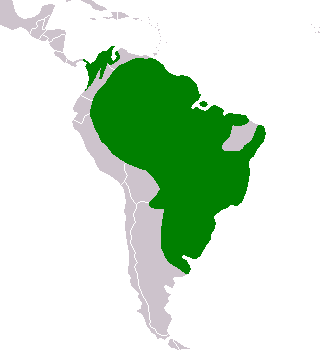
Capybara come from CentralCentral and South America.America. They are semi-aquaticaquatic which means they spend a lot of time in ponds, rivers and lakes, in both savannahssavannahs and rainforests.rainforests.
Diagram of a Capybara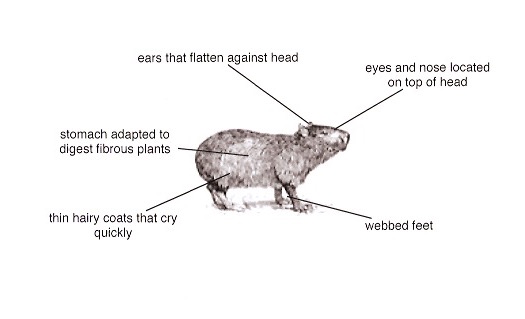
Capybaras' eyes and noses are locatedlocated near the top of their heads. This lets them see and breathe while they are swimming.swimming. They can flattenflatten their ears against their heads to keep water out when they stay submergedsubmerged for up to five minutes. They like to swim and dive and have webbedwebbed feet to help them move easyeasily in the water and on the soft ground. They hide in murkymurky water to get away from hungryhungry predatorspredators like jaguarsjaguars and anacondaanaconda snakes.
Capybara feed on grass and plants that grow near water, eatingeating over three kilograms a day. They feed in the coolerer hours of morningmorning and evening,evening, stayingstaying in the water during the hotterhotter parts of the day. Their stomachsstomachs are speciallyspecially adaptedadapted to let them digestdigest this fibrefibrous plant food. They also eat their own droppingsdroppings (poo)!
 Young capybaras drinking milk from their motherCapybara live in small family groups of about 10 to 20 individuals.individuals. SometimesSometimes the males fight each other to be the dominantdominant male and win the females.females. A capybara pregnancypregnancy lasts for about five months. The babybabies, usually four to five in a litter,litter, are not very good swimmersswimmers so they stay on land, hidehiding under bushesbushes from foxes,foxes, vultures,vultures, wild dogs and piranhas.piranhas. They can live for up to 12 years in zoos but a ten-year-old capybara would be an old one in the wild.
Young capybaras drinking milk from their motherCapybara live in small family groups of about 10 to 20 individuals.individuals. SometimesSometimes the males fight each other to be the dominantdominant male and win the females.females. A capybara pregnancypregnancy lasts for about five months. The babybabies, usually four to five in a litter,litter, are not very good swimmersswimmers so they stay on land, hidehiding under bushesbushes from foxes,foxes, vultures,vultures, wild dogs and piranhas.piranhas. They can live for up to 12 years in zoos but a ten-year-old capybara would be an old one in the wild.
Capybara used to be huntedhunted for their meat and skins but now there are laws restrictingrestricting this.
Glossary
| adapted | changed over time | murky | dirty and dark |
| aquatic | to do with water | rodents | animals like mice, rats, guinea pigs, etc. |
| digest | break down food in the stomach for the body to use | savannah | grassland |
| fibrous | tough, stringy plants, hard to digest | submerged | under the water |
Bibliography
http://switchzoo.com/profiles/capybara.htm
http://www.animalfactguide.com/animal-facts/capybara/
|
Comprehension Clarify these words: located, flatten, webbed, jaguars, anacondas, individuals, dominant, pregnancy, litter, vultures, piranhas, restricting. To help you summarise this animal information report, follow these steps:
What other information would you like to find out about capybara? What connections can you make with this animal report? |
Word Study Verb endings: What happens when we add s, ed and ing to: locate, swim, submerge, dive, web, hide, eat, fight. Other affixes: What happens when we add other prefixes and suffixes like est, en, ly, er, s to these words: big, flat, easy, cool, hot, baby, bush. What two words make up these compound words: rainforest, sometimes. Explain the possessive apostrophe in: capybara’s.
|